ECONOMY
Advanced technology
for better efficiency
How does
a CHP function?
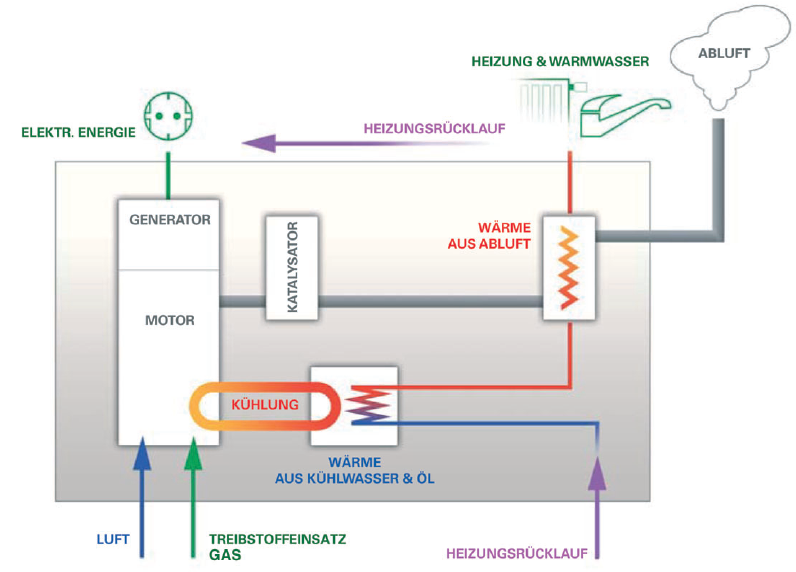
A CHP consists of an engine alternator unit, including the heat exchangers.
That means:
Alternators are driven by gas powered combustion engines.
Normally, the resulting thermal energy remains unused. However, in CHP-units
this energy is being used through heat exchangers and thus reduces heating
cost.
 |
The
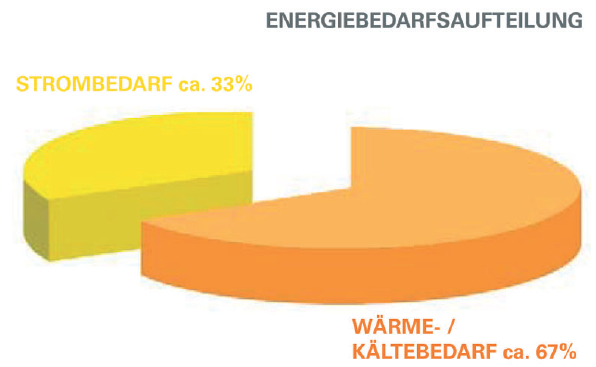
efficiency factor of the unit is calculated as follows: Efficiency factor% = Produced heat and electricity : needed fuel Besides the use of the waste heat, it can also be used via absorption technology to produce cold air for refrigeration. Specially during the summer, excessive waste heat can therefore be used to air-condition buildings. That effect increases the running time and the efficiency of the CHP-unit. |
| For
whom is a CHP useful? CHP-units are excellent to be used for the following: ● Hotels, Restaurants, Indoor pools ● Businesses, Communities, Schools, Public Buildings ● Hospitals, Wellness centers ● Waste water treatment plants ● Bio-gas facilities etc. |
 |
COMPARISON
Traditional facilities and CHP-units in comparison
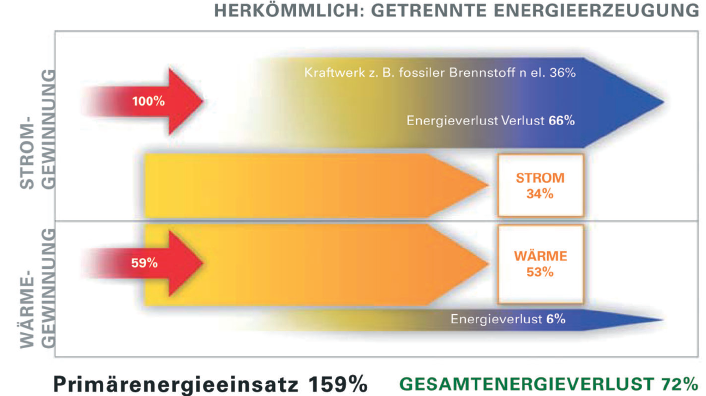 |
With traditional
production of cold air/heat and electricity, large amounts of unused
waste heat and emmissions occur. In addition, consider the low efficiency
factor of traditional units as well as the conduit losses, 30% to
40% of additional primary energy would be required. |
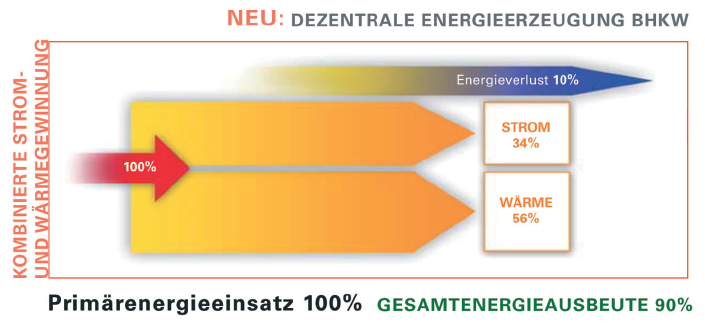 |
With decentralized
energy production in form of a CHP, the overall energy loss is reduced
by using the waste heat of the CHP-unit. |
|